Basic Data Types
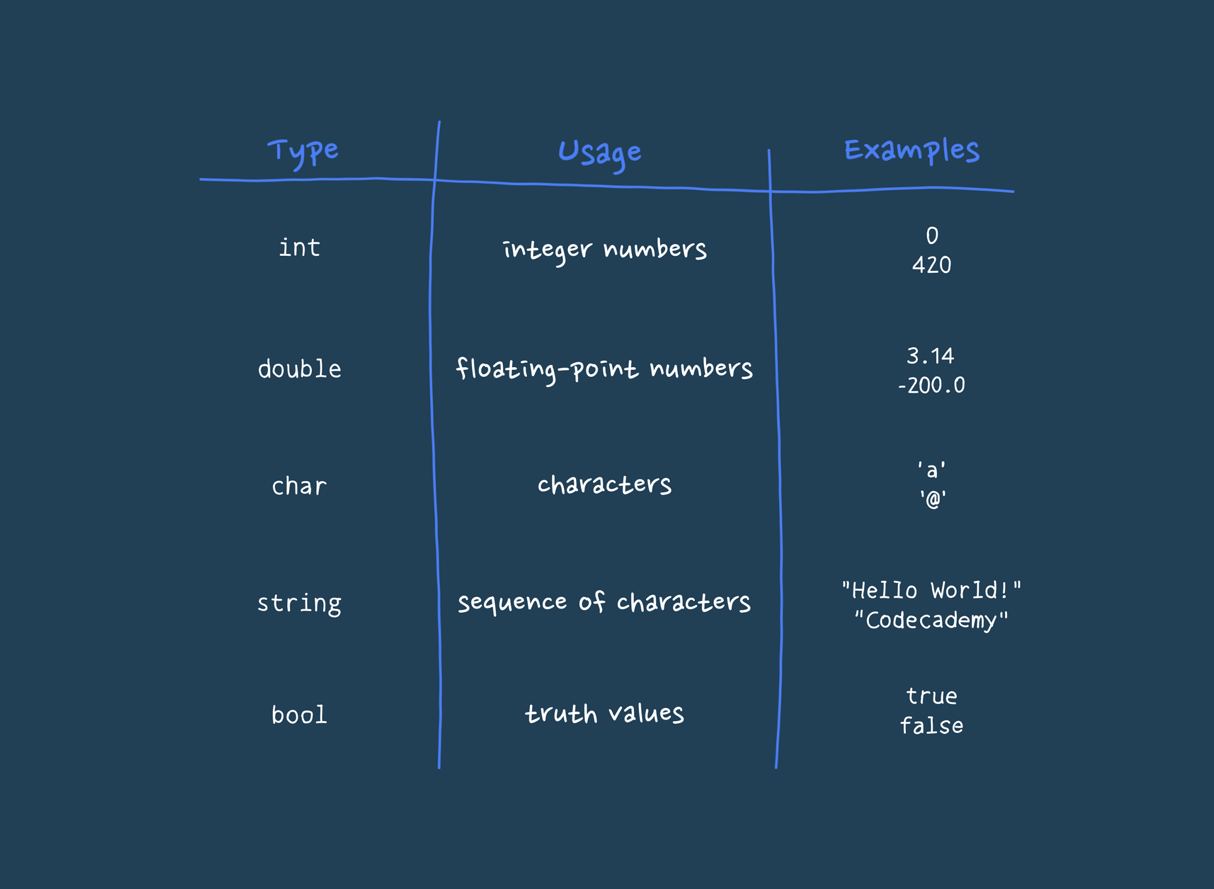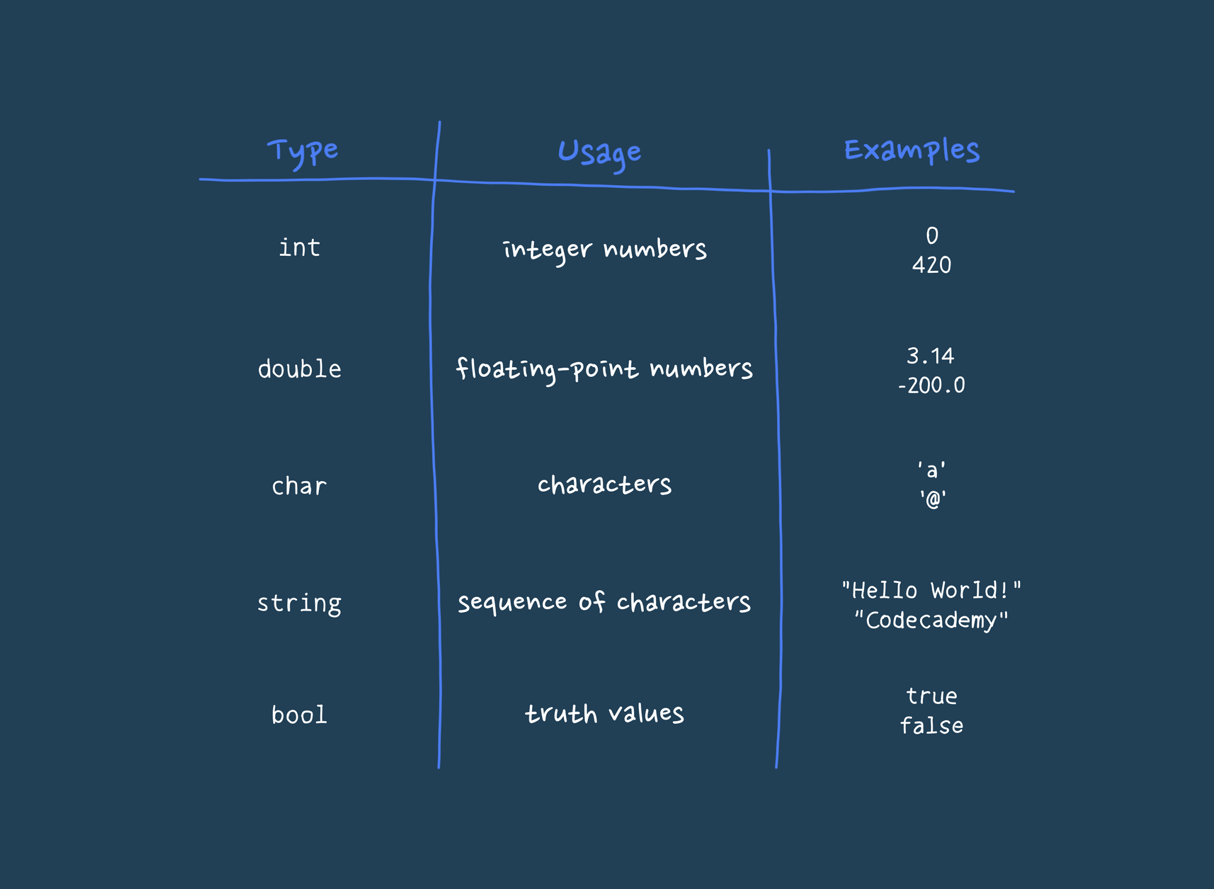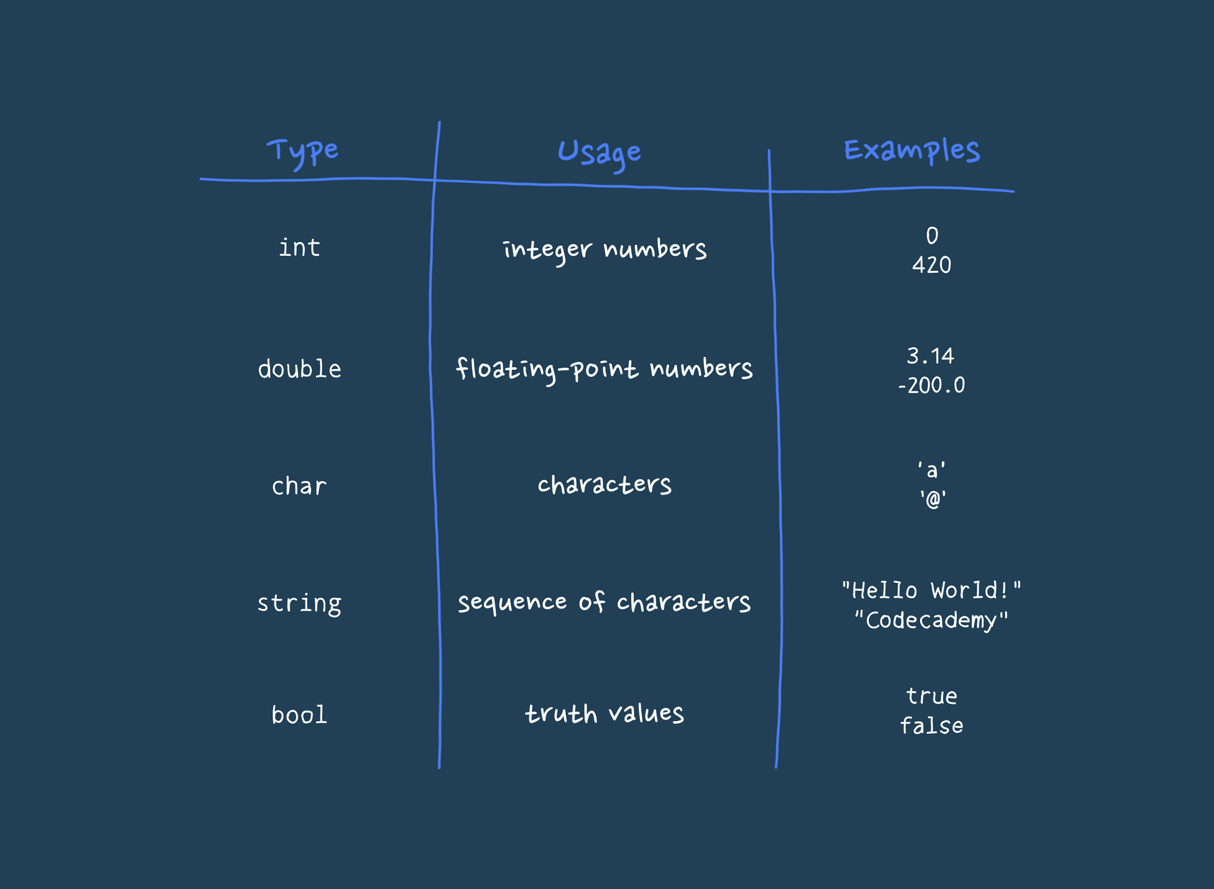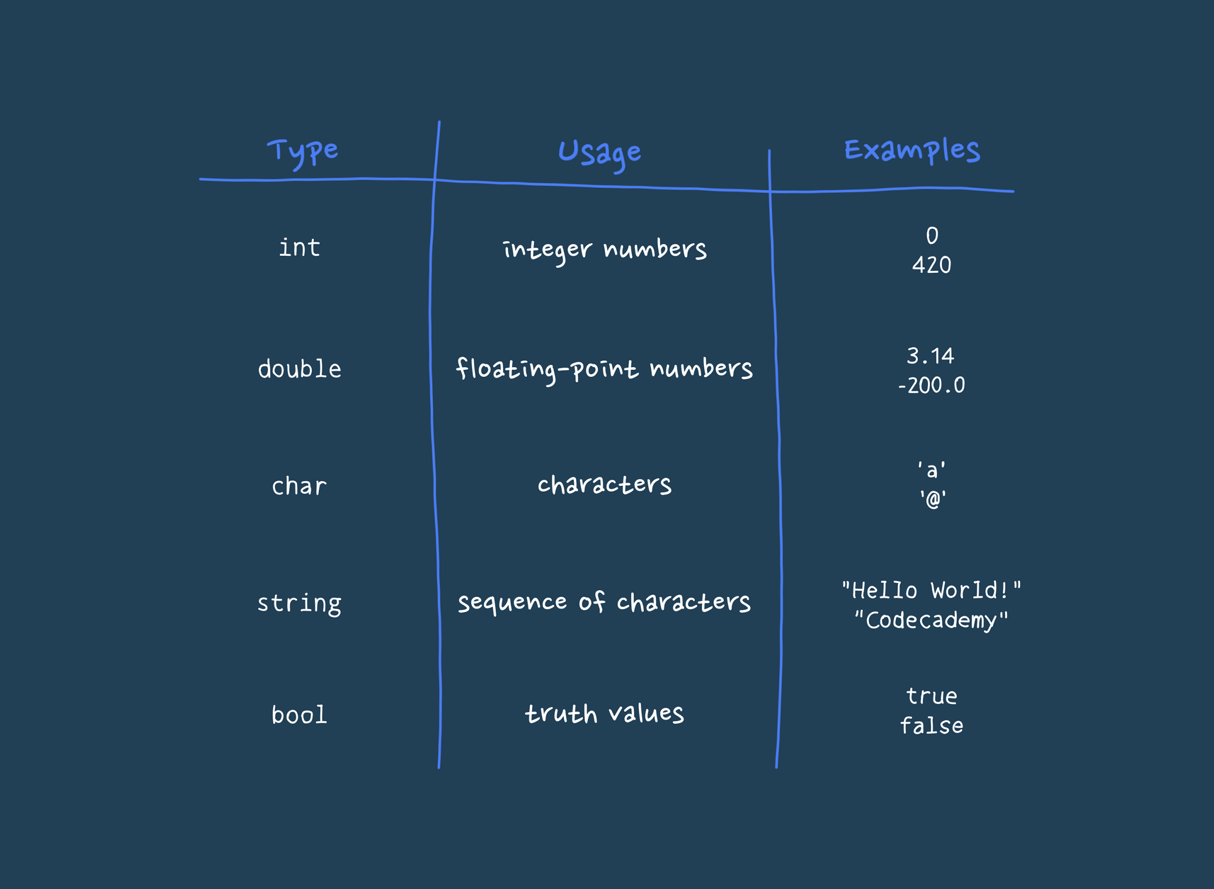
A data type in computer science is a classification that specifies the type of data that a variable can hold and how the data is to be interpreted by the computer. Essentially, it defines the operations that can be performed on the data and the way in which the data is stored in memory. Data types are fundamental in programming languages as they provide a framework for organizing and manipulating data efficiently. Common data types include integers, floating-point numbers, characters, strings, and booleans. For instance, an integer data type would allow a variable to store whole numbers, while a floating-point data type allows for the representation of numbers that have a fractional part. Data types are crucial for ensuring that data is handled correctly by the computer, avoiding errors and making programs more reliable and easier to understand.
Consider a simple example of using data types in a program designed to manage a small business inventory system. In this system, different kinds of data are managed: the number of items in stock (which would be an integer), the price of each item (which could be a floating-point number), the name of each item (stored as a string), and whether the item is currently available for sale or not (represented by a boolean value). For instance, the variable that holds the number of items in stock might be defined as an integer data type, ensuring that it can only store whole numbers like 0, 50, or 200. The price of each item, being potentially non-whole numbers (like $19.99), would be stored as a floating-point data type. The name of each item, such as "Laptop" or "Smartphone," would be stored as a string, a data type used for sequences of characters. Finally, a boolean data type would be ideal for a variable that indicates whether an item is available or not, with values of either true or false. In this everyday example, data types help the inventory system to function correctly by ensuring that each piece of data is handled appropriately—prices can be calculated accurately, stock levels are correctly counted, and product names are properly displayed, all thanks to the correct use of data types.
Understanding data types is crucial for precision and accuracy in programming and data management. Each data type is designed to handle specific kinds of data and to perform particular operations effectively. For instance, using an integer data type for counting items ensures that operations like incrementing or decrementing are performed accurately without errors. If a programmer mistakenly uses a floating-point type for counting items, it could lead to inaccuracies because floating-point numbers are not always precise and can introduce rounding errors. This becomes particularly important in applications such as financial software, where precision is vital for accurate calculations of amounts, interest rates, or transactions. Learning about data types helps ensure that data is stored and manipulated correctly, preventing errors that could lead to incorrect outputs or software malfunctions.
Different data types use different amounts of memory and processing power, which directly affects the efficiency of a program. For example, using an integer data type when only whole numbers are required can be more memory-efficient compared to using a more complex data type like a floating-point number. In contrast, using a floating-point type where fractional values are necessary ensures that calculations involving decimals are handled correctly. Understanding data types helps developers make informed decisions about resource management and optimization. For example, in a mobile app where memory and processing power are limited, choosing the right data type can improve performance and battery life by minimizing memory usage and computation time. Efficient use of data types ensures that applications run smoothly and efficiently, particularly in environments with constrained resources.
Learning about data types is essential for maintaining data integrity and performing effective validation checks. Data types define the kind of data that can be stored in a variable, which helps in validating input data and preventing errors. For instance, if a program requires numerical input for age, using an integer data type ensures that only whole numbers are accepted, rejecting any non-numeric input like text or symbols. Similarly, using a string data type for names prevents numeric values from being mistakenly entered where text is required. Properly handling data types during data validation ensures that the application operates as expected and prevents issues caused by incorrect data entry. This is crucial in systems such as online forms, databases, and user interfaces where data accuracy and validity are paramount.
The string data type is a sequence of characters used to represent textual data. In most programming languages, strings are enclosed in quotation marks. This could be either single quotes (' ') or double quotes (" "), depending on the language. For instance, in Python, you might define a string like this: 'name = "Alice" '. Strings can include letters, numbers, spaces, and special characters. They are used to store and manipulate text in a program. Strings are essential for handling user input, displaying messages, and working with data that is inherently textual. In a real-life scenario, when you fill out a form on a website, the text you enter into fields like "Name" or "Address" is handled as a string. For example, the name "John Doe" would be treated as a string in the system that processes the form. More about String
The integer data type represents whole numbers without any fractional or decimal parts. Integers can be positive, negative, or zero. For example, 'age = 25' or 'temperature = -5' are both integers. In programming, integers are used for counting, indexing, and performing arithmetic operations. They are fundamental to many algorithms and data structures. For instance, when calculating the number of items in a shopping cart or indexing an array to access a specific element, integers are used. In a real-life example, if you are tracking the number of books you own, you would use integers to represent counts like "10 books" or "3 books." More about Integer
The floating-point data type represents numbers that require a fractional part. It includes decimals and is used for more precise calculations that involve real numbers. For instance, 'price = 19.99' or 'temperature = 98.6' are floating-point numbers. This data type is crucial for calculations that require precision, such as financial calculations, scientific measurements, and any operation involving continuous values. In daily life, when you check the weather forecast and see a temperature of 72.5 degrees Fahrenheit, this value is represented as a floating-point number in the program that provides the forecast. More about Floating-Point
The boolean data type represents one of two values: 'true' or 'false'. It is used to perform logical operations and make decisions in a program. For example, a boolean variable could be used to determine if a user is logged in (isLoggedIn = true) or if a condition is met (isAdult = false). Boolean values are fundamental in controlling the flow of a program, such as in if statements, loops, and conditional checks. In a real-life scenario, when a website asks if you want to subscribe to a newsletter and you click "yes" or "no," these responses are handled as boolean values in the backend system. More about Boolean
The character data type represents a single symbol, letter, or digit. It is often used in programming to handle individual characters rather than strings of characters. For example, initial = 'J' assigns the character 'J' to a variable. Characters are useful for processing and manipulating individual letters or symbols, such as when validating a password to ensure it meets certain criteria (e.g., including at least one special character). In a real-life scenario, when you type a single letter into a search box or check the individual characters of a barcode, these characters are processed as character data types in the system. More about Character
In the early days of computing, researchers and engineers introduced primitive data types to define the most basic types of data that could be processed by computers. Primitive data types include integers, floating-point numbers, characters, and booleans. The development of these basic data types was crucial for enabling computers to handle different kinds of data efficiently. For instance, in the 1950s, programming languages like Fortran and COBOL included primitive data types to support mathematical calculations and data management tasks. This foundational work laid the groundwork for more complex data structures and types used in modern programming. More about Primitive Data Types
The concept of abstract data types (ADTs) was formalized in the 1970s by computer scientists like Peter J. Denning and others. ADTs allow programmers to define data types by specifying the operations that can be performed on them, rather than their implementation details. This abstraction is crucial for creating modular and maintainable code. For example, the introduction of ADTs like stacks and queues in programming languages such as Ada and C++ enabled developers to manage data in a more structured way. This research significantly advanced the field of computer science by promoting the design of more flexible and reusable code. More about Abstract Data Types
Type theory, which began developing in the 1960s and 1970s, has had a profound impact on the way data types are understood and used in programming languages. Researchers like Robin Milner contributed to the development of type systems that ensure programs are type-safe, preventing many common errors related to data handling. For example, the creation of the Hindley-Milner type system, which influenced languages like ML and Haskell, provided a robust framework for type inference and type checking. This research has been essential for the development of modern programming languages and compiler design. More about Type Theory
The debate between dynamic and static typing has been a significant area of research in programming language design. Static typing, where data types are checked at compile-time, was exemplified by languages like C++ and Java, ensuring early detection of type-related errors. Dynamic typing, as seen in languages like Python and Ruby, allows for more flexibility by checking types at runtime. Research into these typing systems, including studies on the trade-offs between flexibility and safety, has influenced the design of many contemporary programming languages and their usage in various domains. More about Dynamic and Static Typing
Type inference is a feature in some programming languages that allows the compiler to deduce the type of a variable automatically based on the context in which it is used. This concept gained prominence with the development of languages such as ML and Haskell in the 1980s. Type inference simplifies code by reducing the need for explicit type annotations, making it easier for developers to write and maintain code. The research into type inference algorithms has had a significant impact on the design of modern statically-typed languages and their ability to balance type safety with ease of use.More about Type Inference
Different data types use varying amounts of memory, which can significantly impact the performance and efficiency of a program. For instance, an int in C++ might use 4 bytes, while a char only uses 1 byte. Understanding the memory implications of each data type helps in optimizing the memory usage and overall performance of applications. For example, using smaller data types for large arrays or data structures can save a substantial amount of memory in resource-constrained environments.
Each numeric data type has its own limitations in terms of precision and range. For example, floating-point numbers (e.g., float, double) can introduce rounding errors because of their inherent precision limitations. This can be problematic in applications requiring high precision, such as scientific computations or financial calculations. Choosing the right data type based on the required precision and range is crucial for accurate and reliable results.
Some programming languages are strongly typed, meaning they enforce strict type checking, while others are loosely typed and may automatically convert between types (type coercion). In strongly typed languages like Java, attempting to perform operations on incompatible types will result in compile-time errors, which helps prevent bugs. In contrast, loosely typed languages like JavaScript may perform implicit type conversion, leading to unexpected results if not handled carefully. Understanding these concepts helps in writing robust and error-free code.
Many programming languages allow the creation of custom data types, such as structs in C or classes in object-oriented languages like Java and Python. Custom data types enable developers to model complex data structures and encapsulate data and behavior together. For example, a 'Person' class in Python might have attributes like 'name', 'age', and 'address', along with methods to manipulate this data. This feature enhances code organization and maintainability by allowing developers to define and work with data structures that fit their specific needs.
Implicit and explicit type conversion, or casting, is a critical aspect of handling data types. Implicit conversion occurs automatically when assigning one type to another compatible type, like converting an 'int' to a 'float'. Explicit conversion, on the other hand, requires the programmer to specify the conversion, such as using (int) to convert a float to an int in C++. Mismanagement of type conversions can lead to data loss or runtime errors, so understanding how and when to convert data types is essential for correct and efficient program execution.
1. How did the Hubble Deep Field observation in 1995 change our understanding of the universe?
2. Describe one contribution of ancient Babylonians to early astronomy.
3. Explain the impact of the Islamic Golden Age on the development of astronomy during the medieval period.
4. How did the heliocentric model proposed by Copernicus revolutionize our understanding of the solar system?
5. What are some of the key research areas in contemporary astronomy, and why are they significant?